jupyterlab-vim¶

Notebook cell vim bindings
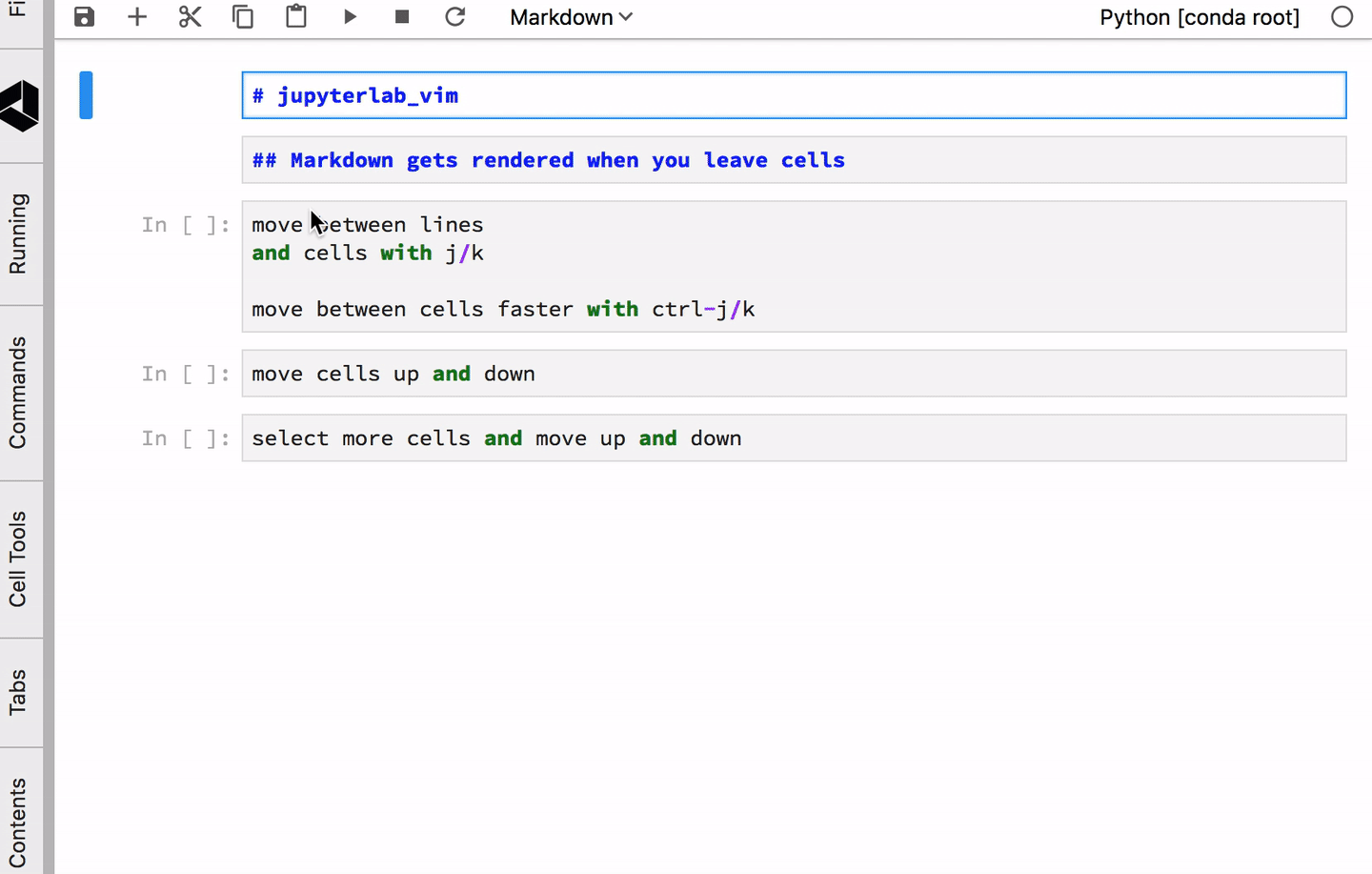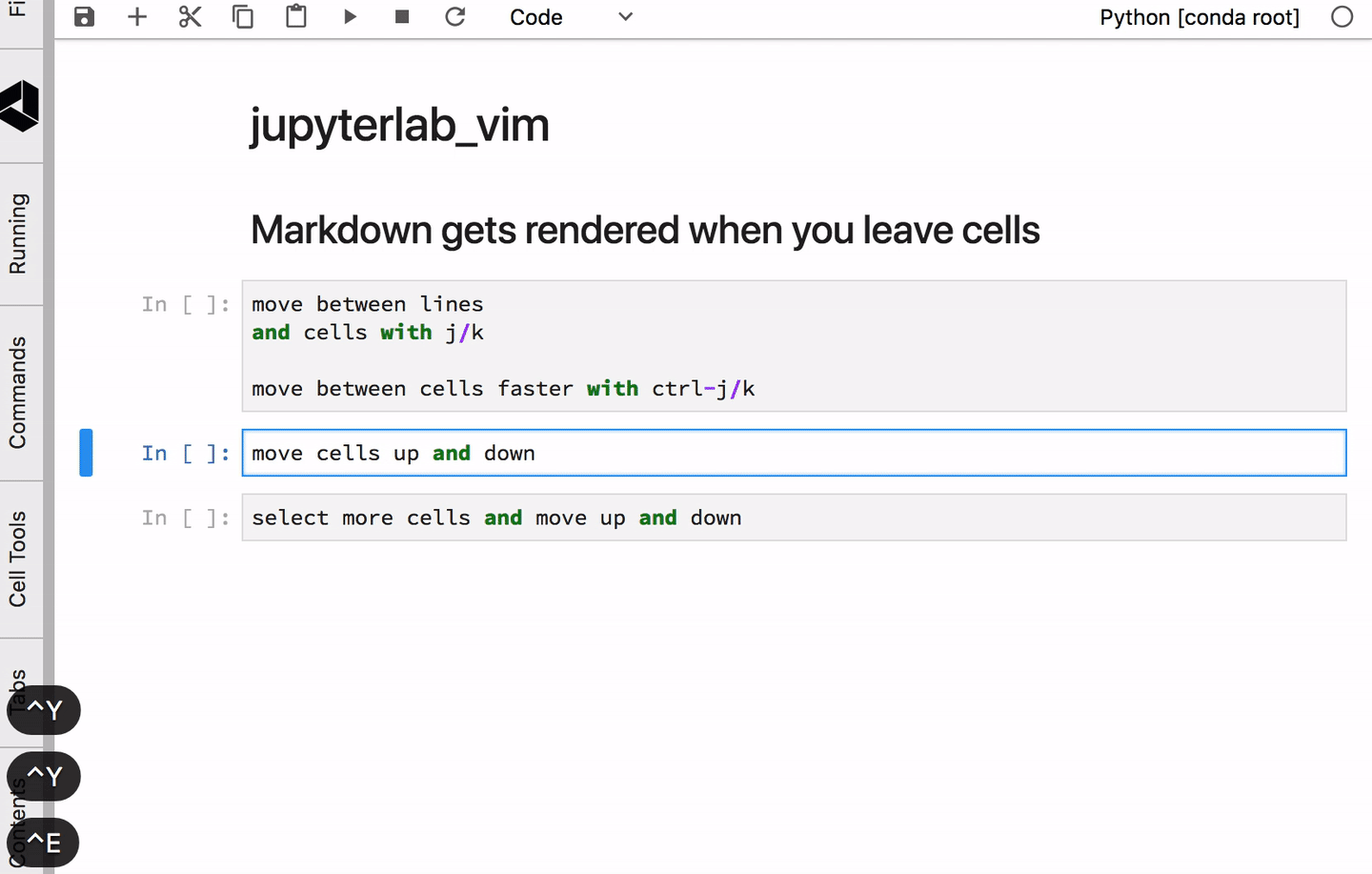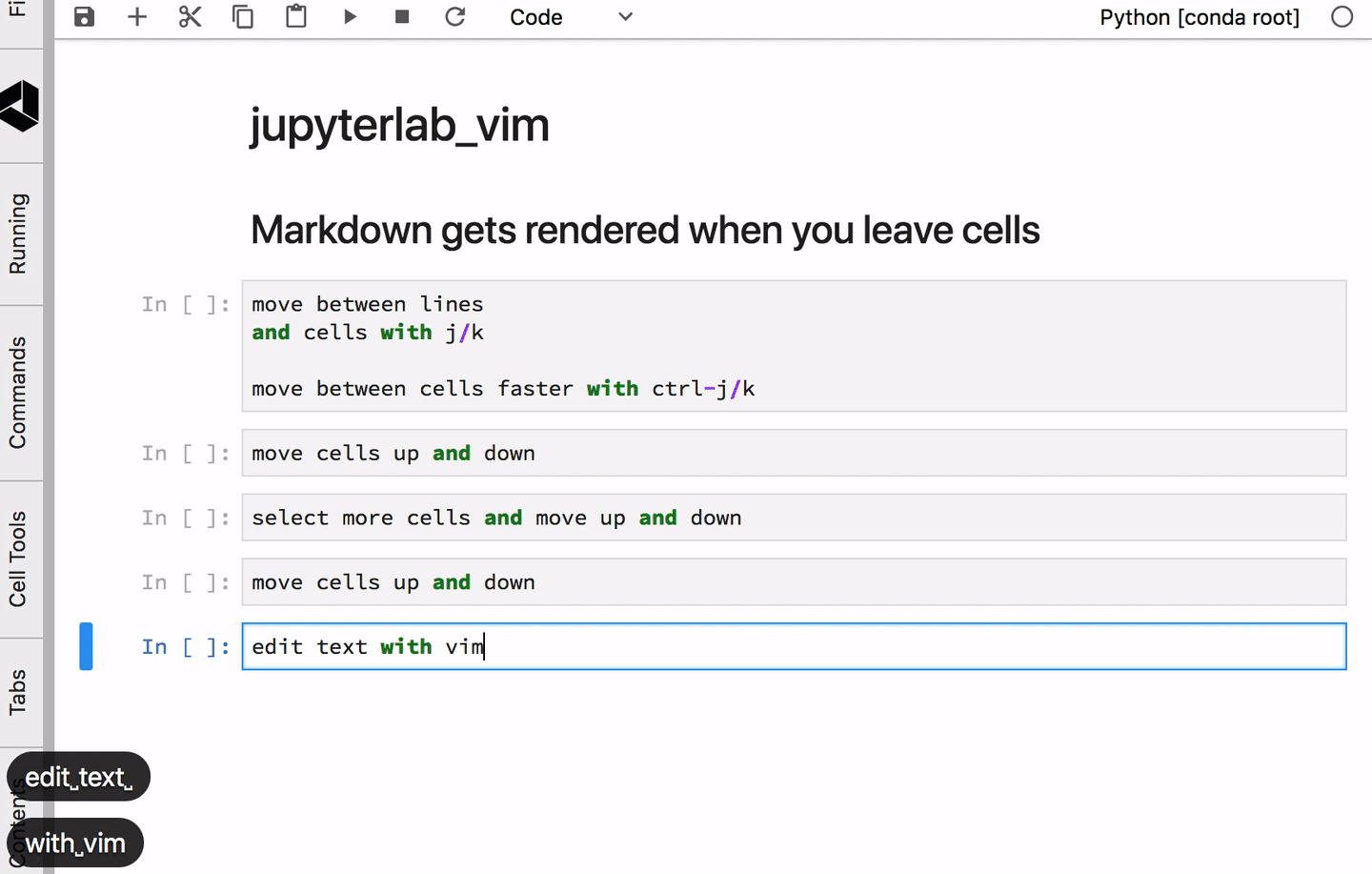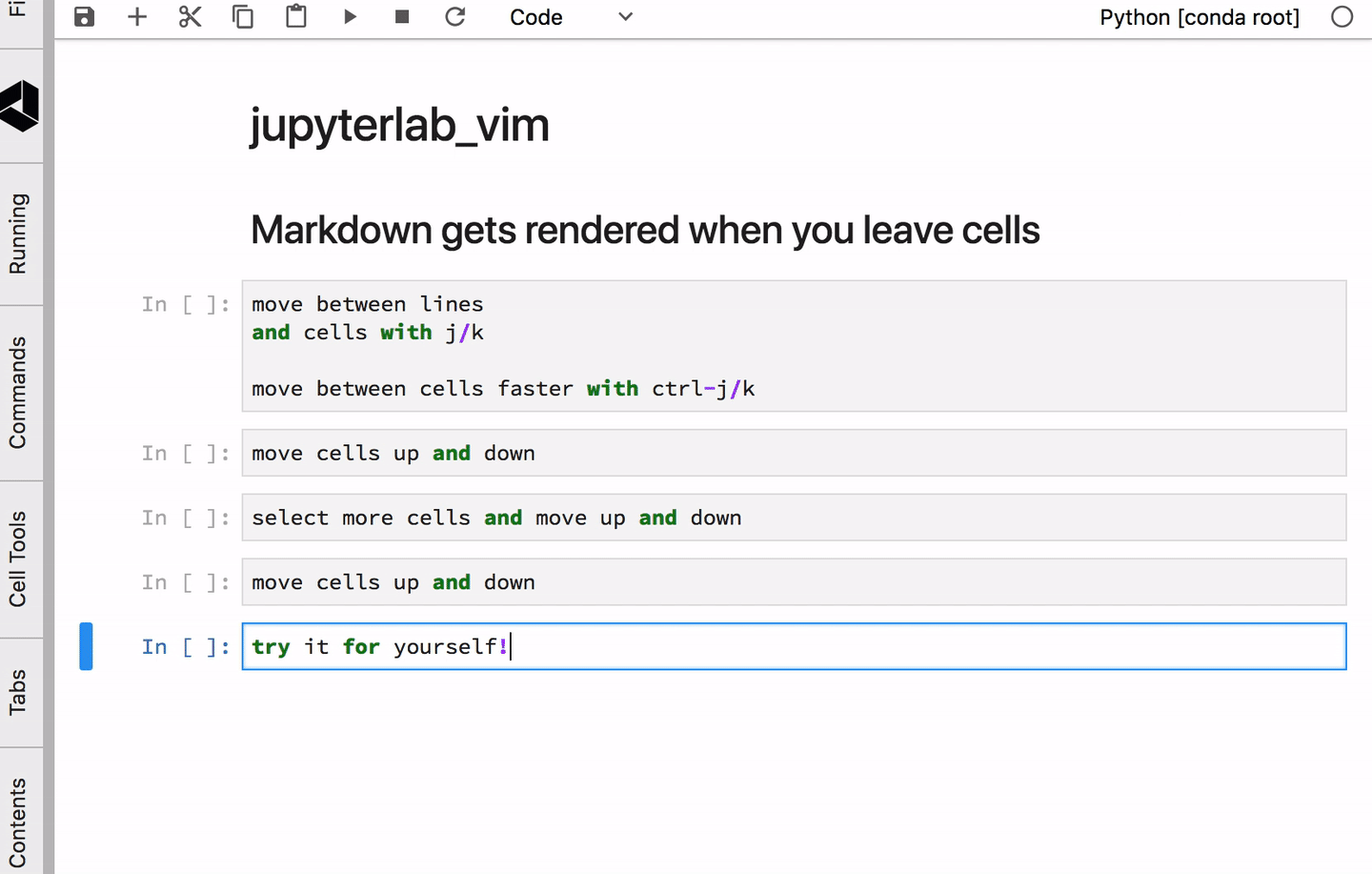
Modes¶
Like vim, Jupyterlab has a distinction between Edit mode and Command mode. Jupyterlab is in Command mode when the cursor is not in a specific cell, and it is in Edit mode when typing in a cell.
This extension combines the Jupyterlab (Edit and Command) modes with the standard vim modes (Normal, Insert and Visual). So the set of modes now looks like:
Jupyterlab Command mode
Jupyterlab Edit mode
Normal
Insert
Visual
Install¶
pip install jupyterlab-vim
or with conda/mamba:
mamba install -c conda-forge jupyterlab_vim
Key Bindings¶
To learn how to modify key bindings see the modify-keybinds.md file.
Please note that all keys are lowercase unless Shift is explicitly indicated. For example, “Y, Y” means pressing lowercase y twice, while “Shift-Y, Y” means pressing Shift+y followed by a lowercase y.
Shortcuts that this extension introduces:
Vim Ex commands¶
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
| :w[rite] | Save Notebook |
| :q[uit] | Enter Jupyter Command Mode |
Vim (Jupyter Edit mode) bindings¶
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
| - | Split Cell at Cursor |
| Ctrl-O, - | Split Cell at Cursor |
| Ctrl-Shift-J | Extend Marked Cells Below |
| Ctrl-Shift-K | Extend Marked Cells Above |
| Ctrl-J | Select Cell Below |
| Ctrl-K | Select Cell Above |
| Ctrl-O, G | Select First Cell |
| Ctrl-O, Ctrl-G | Select Last Cell |
| Ctrl-O, O | Insert Cell Below |
| Ctrl-O, Ctrl-O | Insert Cell Above |
| Ctrl-O, D | Delete (Cut) Cell |
| Ctrl-O, Y | Yank (Copy) Cell |
| Ctrl-O, P | Paste Cell Below |
| Ctrl-E | Move Cell Down |
| Ctrl-Y | Move Cell Up |
| Ctrl-O, U | Undo Cell Action |
| Ctrl-O, Z, Z | Center Cell |
| Ctrl-G | Show Tooltip |
| Cmd/Ctrl-1 | Change to Code Cell |
| Cmd/Ctrl-2 | Change to Markdown Cell |
| Cmd/Ctrl-3 | Change to Raw Cell |
| Shift-Esc | Exit to Command Mode |
| Esc or Ctrl-[ | Exit Current Mode |
Jupyter Command mode bindings¶
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
| G, G | Select First Cell |
| Shift-G | Select Last Cell |
| O | Insert Cell Below |
| Shift-O | Insert Cell Above |
| D, D | Delete (Cut) Cell |
| Y, Y | Yank (Copy) Cell |
| P | Paste Cell Below |
| Shift-P | Paste Cell Above |
| Ctrl-E | Move Cells Down |
| Ctrl-Y | Move Cells Up |
| U | Undo Cell Action |
| Z, Z | Center Cell |
| Z, C | Hide Code Cell |
| Z, O | Show Code Cell |
| Z, M | Hide All Code Cells |
| Z, R | Show All Code Cells |
Switching between modes¶
From Command mode:
To enter Normal mode from Command mode, press Enter.
The extension blocks Shift+Esc from invoking browser commands, such as the browser task manager, by default. To disable the blocking behavior in Command mode, go to Settings menu → Settings Editor → Notebook Vim, and disable the “Override
Shift-Escbrowser shortcut in Jupyter Command mode” option.
From Normal mode:
To leave Normal mode to Command mode, several options are available:
Shift+Esc
Esc or Ctrl+[, if the “Enable
EscandCtrl-[leaving vim Normal mode to Jupyter Command mode” option is enabled (on by default). To disable the option, go to Settings menu → Settings Editor → Notebook Vim.
To enter Insert mode from Normal mode, use one of the insert commmands, such as i, Shift+i, a, Shift+a, o, Shift+o, c, Shift+c, s or Shift+s.
To enter Visual mode from Normal mode, use one of the visual commands, such as v, Shift+v or Ctrl+v.
From Insert or Visual mode:
To leave Insert or Visual mode to Normal mode, press Esc or Ctrl+[.
To leave Insert or Visual mode to Command mode, press Shift+Esc.
Special Thanks¶
From @jwkvam:
I want to acknowledge Alisue and his excellent work creating vim bindings for Jupyter notebooks. I hope this extension can meet the high bar his work set.
@jkwvam is the original author of this extension - the original version can be seen here. When that version was not updated it was updated first by @axelfahy and then moved to this community organization.
Contributing¶
Contributions and feedback are most welcome!
Development install¶
Note: You will need NodeJS to build the extension package. To install with conda do:
conda install -c conda-forge nodejs
The jlpm command is JupyterLab’s pinned version of
yarn that is installed with JupyterLab. You may use
yarn or npm in lieu of jlpm below.
# Clone the repo to your local environment
# Change directory to the jupyterlab_vim directory
# Install package in development mode
pip install -e .
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension develop . --overwrite
# Rebuild extension Typescript source after making changes
jlpm run build
You can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension’s source and automatically rebuild the extension.
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
jlpm run watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter lab
With the watch command running, every saved change will immediately be built locally and available in your running JupyterLab. Refresh JupyterLab to load the change in your browser (you may need to wait several seconds for the extension to be rebuilt).
By default, the jlpm run build command generates the source maps for this extension to make it easier to debug using the browser dev tools. To also generate source maps for the JupyterLab core extensions, you can run the following command:
jupyter lab build --minimize=False
Uninstall¶
pip uninstall jupyterlab_vim




